Dingfang Hu, Rongrong Huang,* and Yu Fang*. Precis. Chem. 2024, DOI: 10.1021/prechem.4c00072
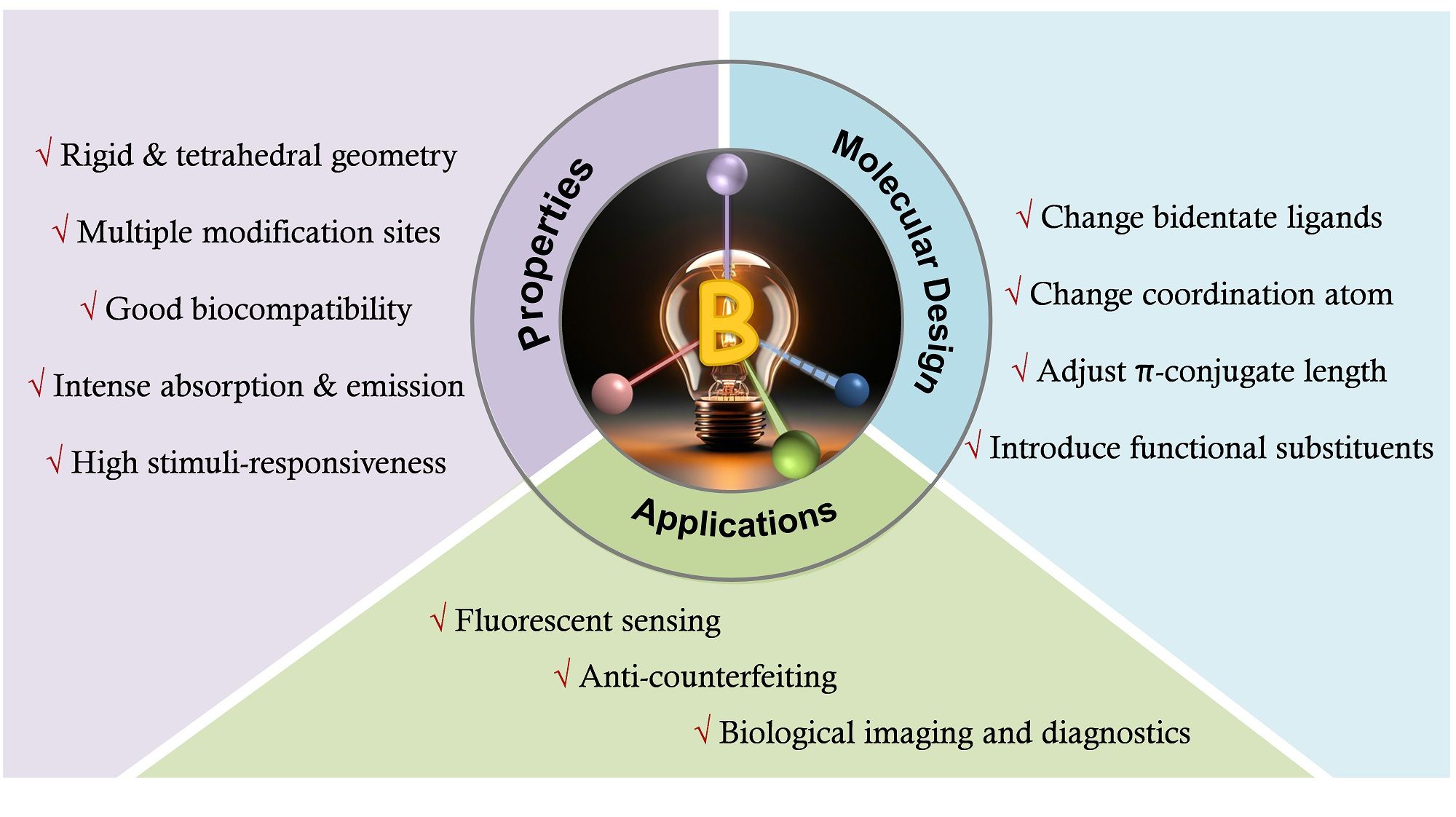
Figure 1. Overview of Topics on Tetra-Coordinate BoronBased Photoactive Materials
Tetra-coordinate boron-based fluorescent materials hold considerable promise across chemistry, biology and materials science due to their unique and precisely tunable optoelectronic properties. The incorporation of the heteroatom boron (B) enables these materials to exhibit high luminescence quantum yields, adjustable absorption and emission wavelengths, and exceptional photostability. The distinctive properties of tetra-coordinate boron-based photoactive molecules arise primarily from the electron-deficient nature of the boron center, which facilitates efficient interactions with conjugated systems, and thereby enhances electron delocalization and charge transfer processes.
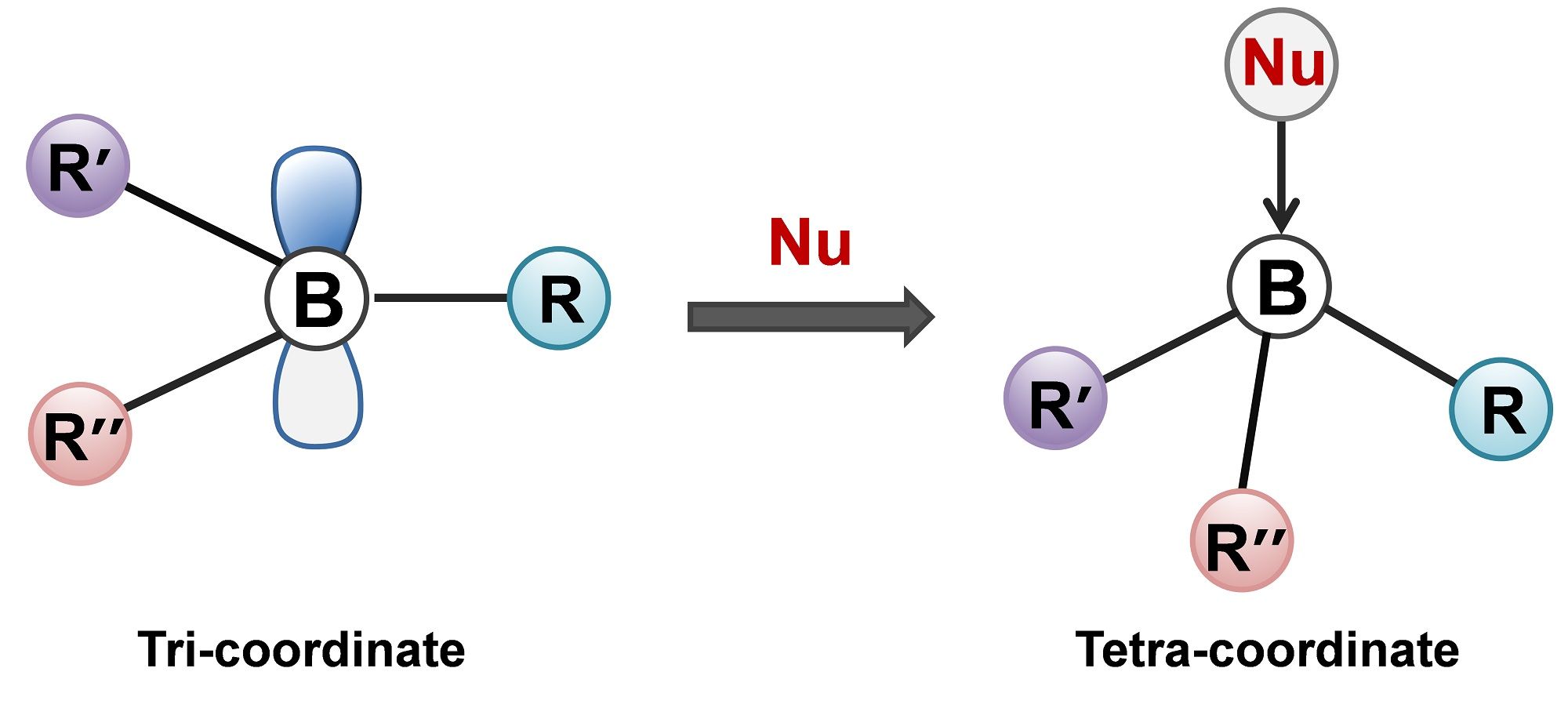
Figure 2. Schematic illustration for the tricoordinate organoboron compounds and the tetra-coordinate organoboron compounds. Nu represents nucleophile, the three substituents (R, R’, R’’) can be identical or differ from one another.
This review examines the molecular design and applications of tetra-coordinate boron-based photoactive molecules. We outline how structural features impact their properties and discuss strategies for enhancing their performance, including ligand modification and the extension of conjugation length, among others. Additionally, we will emphasize their emerging roles in luminescent sensing, anticounterfeiting, and luminescent imaging, and identify the challenges and future directions in this rapidly evolving field.
First Author: Hu Dingfang, doctoral candidate, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Authors: Postdoctoral Researcher Huang Rongrong, Singapore University of Technology and Design; Prof. Fang Yu, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: https://doi.org/10.1021/prechem.4c00072
 Latest Updates
Latest Updates






