Lu Liu, Sheng Li, Nan Zhang, Qiyuan Shi, Ke Liu, Taihong Liu*, Zhiyan Huang*, Liping Ding, and Yu Fang. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2023, 127, 10171−10178.
Emerging excited-state dynamics and structure−property correlations have driven the efforts to develop novel chromophores incorporating various electron-donating and electron-accepting moieties. Basically, an attractive photophysical phenomenon is intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) throughout the conjugated molecular skeleton. Various models for the ICT dynamics have been proposed to verify distinguishable spectral features such as dynamic Stokes shift (DSS), fluorescence lifetime change, and varied emission ratios. The DSS reflects the evolving frequency shift between absorption and emission maxima of a chromophore and its surrounding microenvironment. Therefore, related charge redistribution altered by electronic excitation and the ensuing adjustment of the configuration could be unveiled in the time-dependent DSS. The BODIPYs tend to reorganize and generate new conformations possessing narrow energy gaps. The corresponding change normally results in a time-resolved spectral shift, which is dependent on the surrounding solvent polarity and relaxation time scale. Therefore, it is important to understand the structure-property correlations and its influence on the dynamics of excited states through BODIPY derivatives.
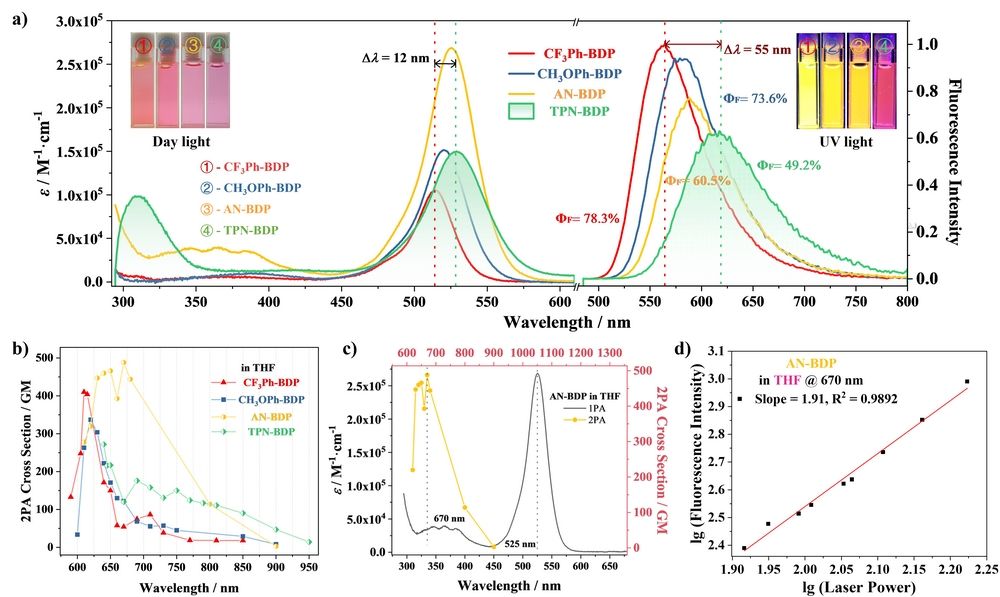
Figure 1. (a) UV−vis absorption and normalized emission spectra of the triads in THF (c ∼ 1.0 × 10−6 M). (b) Summarized and comparative 2PA spectra of the triads in THF. (c) Combined 1PA and degenerate 2PA spectra of AN-BDP as an example in THF. (d) Quadratic dependence of the two-photon excited fluorescence intensity of AN-BDP in THF on the incident laser power at fs-670 nm.
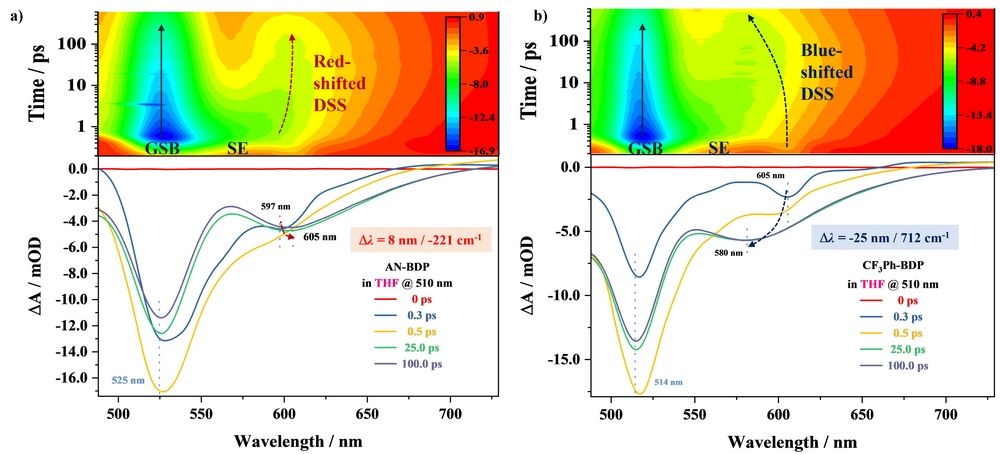
Figure 2. Time-resolved and wavelength-resolved DSS characteristics of AN-BDP (a) and CF3Ph-BDP (b) in THF. The arrows highlighted the time-dependent and shifted SE signals.
This work designed and synthesized a series of diaryl BODIPY derivatives with 2,6 different substituents. Based on the spectral shifts that change with time when the new conformation of these molecules from the ground state to the excited state, they extracted the dynamic Stokes shifts. Strikingly, evolution dynamics in high spatial and temporal resolutions of the excited states and structure-property correlation of the triads were first obtained systematically and comprehensively. Especially, the blue-shifted DSS and the structure−property correlations were elucidated comparatively. Specifically speaking, at the early excited stage, AN-BDP and TPN-BDP with strong electron donating and efficient charge separation capabilities, the SE band at 597 nm of AN-BDP in THF red-shifted considerably to 605 nm after a time constant of 100 ps (Δl ~ 8 nm/-221 cm-1) (Figure 2a). A similar and enlarged red shift (Δλ ∼ 25 nm/-652 cm−1) for TPN-BDP was confirmed. This work held that the energy level of PICT2 was slightly higher than that of the final CT state. By contrast, that of CF3Ph-BDP blue-shifted from early 605−580 nm (Δλ ∼ −25 nm/712 cm−1) with a small blue-shift value for CH3OPh-BDP (Δλ ∼ −18 nm/507 cm−1) with a relatively weak CT character. Therefore, the blue-shifted DSS was rationalized to be the sequence conversion between the corresponding PICT1 and CT states controlled by structural planarization, which was confirmed by the theoretical calculations mentioned above. Besides, much more red-shifted values for AN-BDP in polar DMSO and DMF were observed, consistent with the typical DSS measurements in terms of the polar solvations. They speculated that the population of the PICT state was strongly affected by its stabilized conformations, and the main contribution to ultrafast dynamics stemmed from the ultrafast rearrangement and CT degree. The significant findings in the present work will further deepen the exploration of the optoelectrical properties and technological applications of such BODIPY derivatives.
First Authors: Liu Lu and Li Sheng, Master’s candidates, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Authors: Assoc. Prof. Liu Taihong and Huang Zhiyan, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c06757
 Latest Updates
Latest Updates






