Nan Zhang, Lu Liu, Haixia Chang, Ke Liu, Taihong Liu*, Liping Ding, and Yu Fang. J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2023, 14, 7283-7289.
Multipolar chromophores and corresponding aggregates have gained ever-expanding attention owing to the feasibility of charge delocalization and energy level engineering. Complicated theories based on the Frenkel exciton theory and Kasha model have been developed on understanding the aggregation of polarizable chromophores. Unconventional non-Kasha behaviors have been observed where Frenkel excitons can strongly couple to intermolecular excitons and in certain packing morphologies give rise to distinct aggregates. Besides, a richer array of aggregate. Although considerable discussion on photophysical dynamics of molecular aggregates is revitalized, in-depth studies of aggregates are still limited by the small family of suitable materials or infrequent packing arrangements.
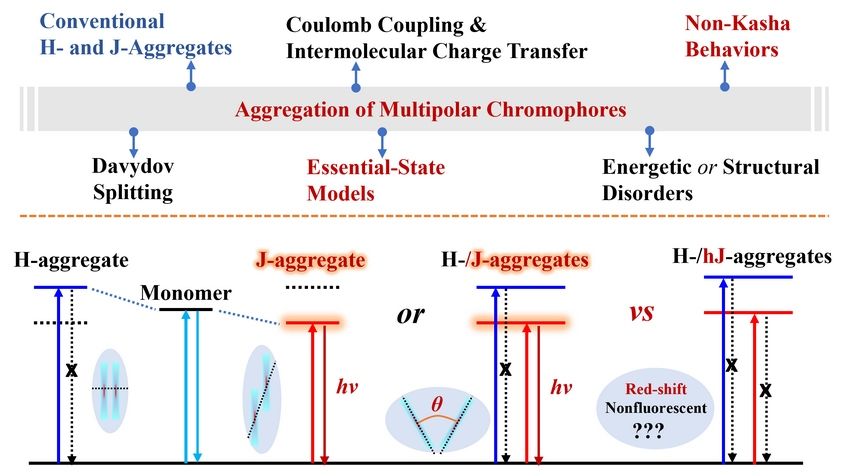
Figure 1. Diverse theories and representative energy transitions on understanding the aggregation phenomena of multipolar chromophores.
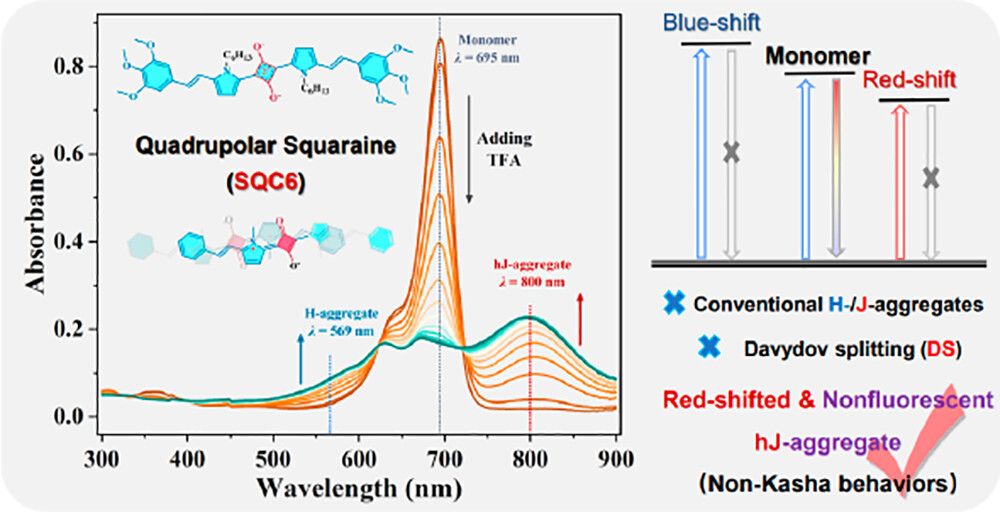
Herein, we obtained the new quadrupolar squaraine compound, distinct aggregates of SQC6 in the presence of TFA were comparatively demonstrated in different organic solvents. Subtle changes of the solvent and ion pair influenced the aggregation of SQC6 and led to the significant variations in optical properties. The stabilization of the dimer suggested strong exciton coupling with the adjacent molecules initiated by the π-π stacking and electronic interaction. Vanishment of the dimer and generation of the nonfluorescent red-shifted hJ aggregate were elucidated well based on the ESM model. Additionally, comparative fs-TA studies confirmed the notable differences in relaxation dynamics and the importance of the CT state. Fast relaxation processes in the excited state might be associated with CT processes upon electronic excitation. Broadband 2PA and the maximum 2PA cross section manifested the intrinsic resonance-enhanced characteristics of squaraine derivatives. The strength of excitonic coupling directly addressed the position of absorption bands, and thus, pronounced excitonic interactions could favor noticeable enhancement of 2PA efficiency. Present results contribute to the understanding of the nature of specific intermolecular interactions and open new perspectives in constructing tunable aggregates with unusual packing models and unique optical properties.
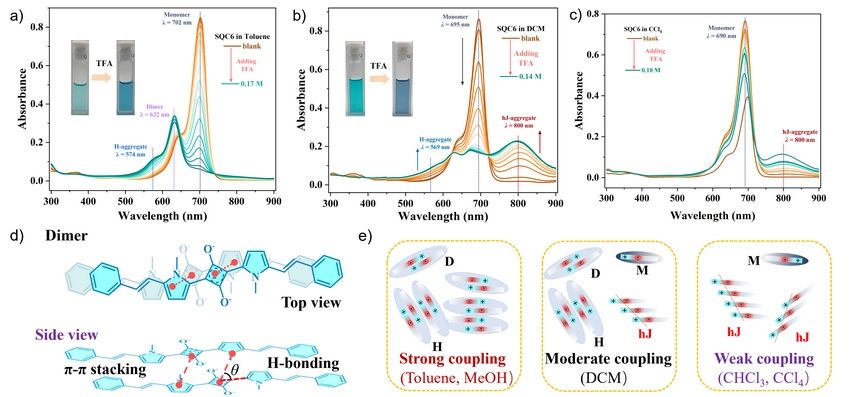
Figure 2. Absorption spectra changes of SQC6 in (a) toluene, (b) DCM, and (c) CCl4 in the presence of various concentrations of TFA. The inset showed the solution color changes before and after adding TFA. (d) Schematic illustration of the two views of dimer fragments. (e) Distinct aggregation of SQC6 cooperated by TFA in different media with diverse coupling strength.
First Author: Zhang Nan, Master’s candidate, Shaanxi Normal University
Correspondence Author: Assoc. Prof. Liu Taihong, Shaanxi Normal University
Full Text Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c02029
 Latest Updates
Latest Updates






